
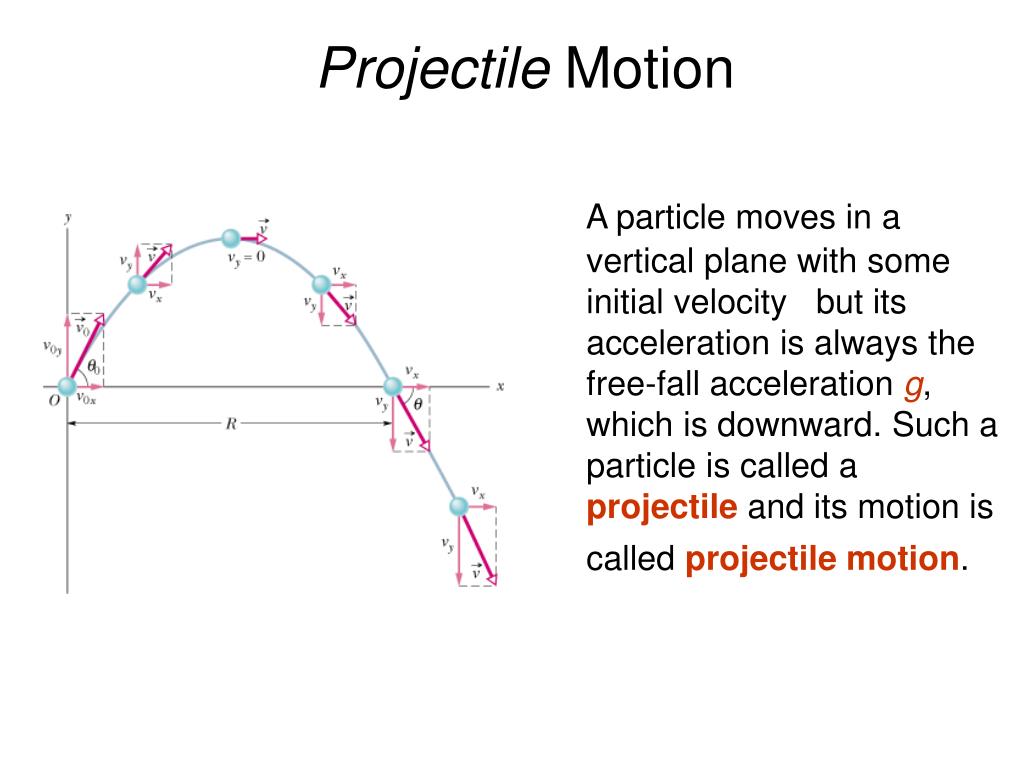
The only mathematically significant force acting on the object is gravity, which operates downward, imparting a downward acceleration on the object towards the Earth’s centre of mass. Ballistics is the study of such motions, and such a trajectory termed a ballistic trajectory. Galileo demonstrated that this curving path is a parabola, although it can also be a straight line when thrown directly above. Projectile motion is a type of motion that an item or particle (a projectile) experiences when it is projected near the Earth’s surface and moves along a curved route only under the influence of gravity (in particular, the effects of air resistance are passive and assumed to be negligible).

Example 1Ī basketball player throws a ball from some distance making the projectile motion. And if the projectile motion is given, we can calculate any term from gravitational acceleration, initial velocity, and time.Īn online vertical velocity calculator can be used to find the projectile motion, gravitational acceleration, initial velocity, and time. To calculate the projectile motion, we must have gravitational acceleration, initial velocity, and time.

Scientists make experiments by taking the calculation and throwing the object either it reaches or not to the required destination or not just with the help of the formula.
The calculation for throwing the objects away can easily be done with the help of the formula.

In the above equation, h is the height of the object from where the object is thrown, t is the time, and g is the gravitational acceleration. To determine the distance of the vertical components of the velocity for projectile motion can be written as. This acceleration experiences the force of gravity and must be equal to 9.8m/sec 2. In simple words, when an object is thrown upward there must be an unbalanced force that acts on the object and it will accelerate downward. The vertical components of the projectile motion are handled by the force of gravity. In the above equation, v is the constant velocity and t is the time taken by the motion. To determine the distance of the horizontal components of the velocity for projectile motion can be written as. The range of the projectile must be the same if an object is projected at the constant starting speed with the two opposite angles. The range of the object or the projectile is the horizontal displacement of the projectile and it is dependent on the initial velocity form where the abject is launched.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
